Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) is expanding at a rapid pace. From smart homes to industrial automation, billions of devices are connecting to the internet every year. Yet, one of the most important choices for any IoT solution is how devices communicate with the cloud and with each other.
Choosing the right IoT protocol is critical. Two of the most widely discussed protocols are LwM2M (Lightweight M2M) and MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport). Each has strengths and weaknesses, and the decision depends on the specific requirements of your IoT application.
In this blog, we will explore both protocols in depth, compare their features, and provide guidance on which one is best for different IoT solutions. By the end, you’ll have a clear framework for deciding between LwM2M vs MQTT for your IoT projects.
What Is MQTT?
Overview
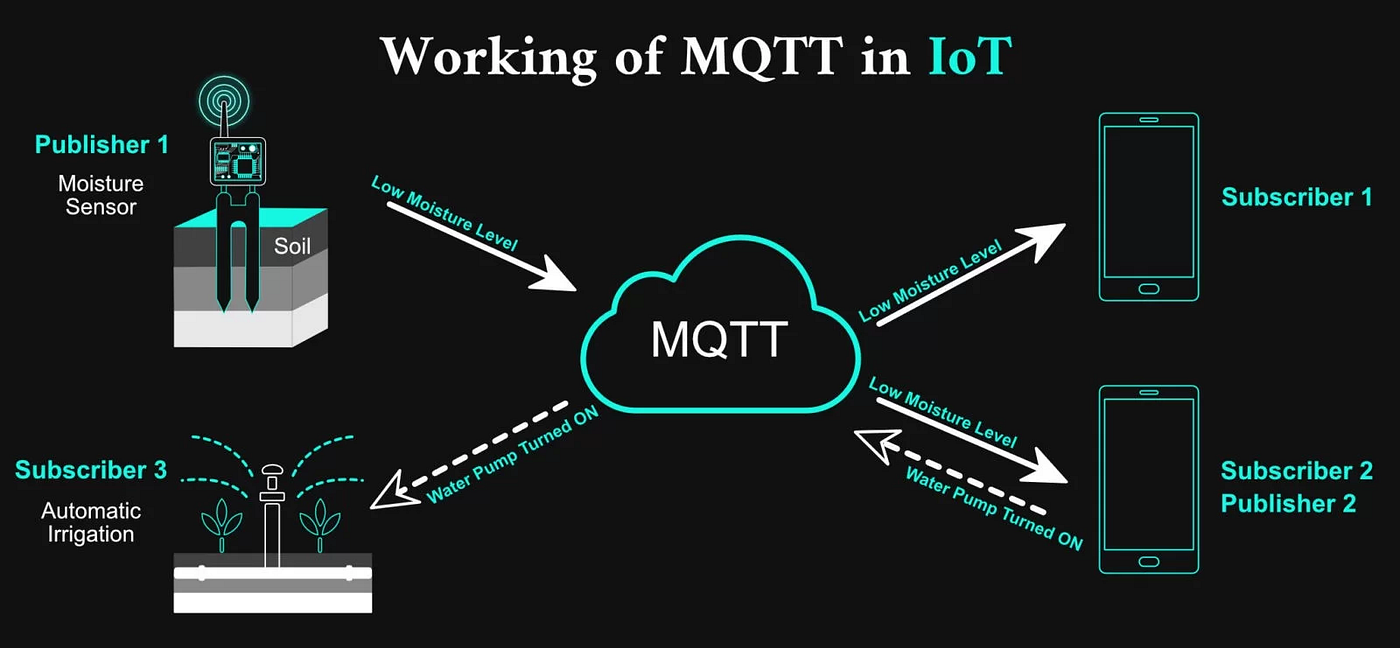
MQTT, short for Message Queuing Telemetry Transport, is a lightweight publish/subscribe messaging protocol designed in the late 1990s by IBM. It was originally created to monitor oil pipelines over unreliable satellite networks.
Key Characteristics of MQTT
- Lightweight: Minimal packet size, making it efficient for low-bandwidth networks.
- Publish/Subscribe Model: Devices publish messages to topics, and subscribers receive updates without direct connections.
- Reliable Messaging: Supports Quality of Service (QoS) levels:
- QoS 0: At most once
- QoS 1: At least once
- QoS 2: Exactly once
- Protocol Simplicity: Easy to implement, widely supported by IoT platforms.
Typical Use Cases for MQTT
- Smart home devices (lights, thermostats, alarms)
- Asset tracking with IoT SIM cards
- Industrial IoT sensors transmitting telemetry
- Connected cars sending real-time status updates
What Is LwM2M?
Overview
Lightweight Machine-to-Machine (LwM2M) is a device management protocol developed by the OMA SpecWorks. It runs over CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) and is specifically designed for managing constrained IoT devices.
Key Characteristics of LwM2M
- Device Management: Built-in functions for provisioning, configuration, and firmware updates.
- Efficient Data Encoding: Supports CBOR and SenML, making it efficient for IoT communication.
- Security: Uses DTLS for secure data transmission.
- Standardized Data Models: Predefined objects make interoperability easier.
- Supports Constrained Devices: Optimized for low-power, low-memory IoT devices.
Typical Use Cases for LwM2M
- Smart meters and utility devices
- Large-scale IoT deployments with thousands of devices
- Remote firmware updates for IoT gateways
- Industrial sensors requiring lifecycle management
LwM2M vs MQTT: A Feature Comparison
| Feature | MQTT | LwM2M |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Publish/Subscribe messaging | Device management & messaging |
| Transport Layer | TCP (or WebSocket) | UDP/CoAP |
| Security | TLS | DTLS |
| Efficiency | Lightweight but overhead with TCP | More efficient with UDP |
| Device Management | Limited | Built-in (provisioning, updates) |
| Scalability | High (millions of messages per second) | Strong for device lifecycle management |
| Ease of Implementation | Very simple | More complex |
| Use Cases | Real-time telemetry, event-driven apps | Remote device management, constrained IoT networks |
The Role of IoT SIM Cards in LwM2M and MQTT
When IoT devices connect via IoT SIM cards, the choice of protocol becomes even more critical.
- With MQTT over cellular IoT SIM cards, devices send frequent small packets. The reliability of TCP ensures message delivery, but may consume more bandwidth.
- With LwM2M over cellular IoT SIM cards, devices use UDP-based communication, which reduces overhead and data costs, making it more efficient for large-scale deployments.
👉 For businesses using global IoT SIM cards (like those from Zhongyi IoT), protocol efficiency directly impacts both performance and cost savings.
Strengths and Weaknesses of MQTT
Strengths
- Simple and widely adopted
- Flexible publish/subscribe model
- Works well with real-time IoT applications
- Strong community support and libraries
Weaknesses
- Limited device management capabilities
- TCP overhead increases bandwidth consumption
- Not optimized for very constrained devices
Strengths and Weaknesses of LwM2M
Strengths
- Built-in device management (firmware updates, provisioning)
- UDP-based, making it bandwidth-efficient
- Supports low-power devices
- Strong standardization for interoperability
Weaknesses
- More complex to implement
- Smaller community compared to MQTT
- Limited adoption in consumer IoT devices
When to Choose MQTT
MQTT is the best choice if your IoT solution:
- Requires real-time messaging (e.g., alarms, sensors, connected cars)
- Uses devices with sufficient power and memory
- Needs flexible message routing through a broker
- Prioritizes ease of integration with cloud platforms
When to Choose LwM2M
LwM2M is the best choice if your IoT solution:
- Requires remote device management at scale
- Needs efficient communication over constrained networks (NB-IoT, Cat-M1)
- Involves devices with limited power and resources
- Focuses on lifecycle management (provisioning, configuration, updates)
Hybrid Approach: Using MQTT and LwM2M Together
In some cases, the best solution is not choosing one over the other, but combining both:
- Use MQTT for telemetry data (e.g., temperature, video events).
- Use LwM2M for device management (e.g., provisioning, firmware upgrades).
Many IoT platforms already support hybrid models, ensuring businesses can leverage the strengths of both protocols.
Future Trends: LwM2M, MQTT, and 5G IoT
With the rise of 5G, edge computing, and global IoT SIM cards, both protocols are evolving:
- MQTT is being optimized for massive IoT telemetry.
- LwM2M is adding features for AIoT device lifecycle management.
- Cloud providers (AWS IoT, Azure IoT, Google Cloud IoT) are expanding support for both.
The future may not be “MQTT vs LwM2M” but rather “MQTT + LwM2M + 5G” as complementary technologies.
Zhongyi IoT: Empowering IoT Solutions with Global Connectivity
At Zhongyi IoT, we provide global IoT SIM card solutions that make both MQTT and LwM2M deployments possible. Whether your devices require real-time telemetry or lifecycle management, our IoT SIM cards ensure:
- Global Multi-Network Coverage (600+ operators in 190+ countries)
- Secure Private APN and VPN Support
- Centralized SIM Management Platform
- Custom Data Plans to Reduce Costs
With the right connectivity partner, your choice of IoT protocol becomes even more powerful.
Conclusion: Which Protocol Is Best?
So, LwM2M vs MQTT — which is best for IoT solutions?
The answer is: it depends.
- Choose MQTT if your focus is real-time messaging and telemetry.
- Choose LwM2M if you need scalable device management and efficiency.
- Choose both if you want a hybrid approach that combines strengths.
In the end, the protocol is only one part of the IoT puzzle. Reliable global connectivity, like that provided by Zhongyi IoT SIM cards, ensures that your devices stay online, secure, and cost-efficient — regardless of the protocol you choose.
📞 Contact Zhongyi IoT today to explore how our IoT SIM card solutions can power your MQTT or LwM2M-based IoT deployments.